CARE IN MOTION with The Invisible Disabilities Association®: Post-Vaccine Injury and SUDDEN DEAFNESS - A Reversible MEDICAL EMERGENCY if Treated in 2-4 Weeks
After Vaccination, Not Only a Study Show a 2X Increase in Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss Double in the Elderly, Those with Risk Factors for Hearing Loss are Pushed "Over the Edge"" by Vaccination
This Martin Luther King Holiday, I am grateful that we made it this far, that we can walk and talk, read and write. I am also grateful for those like Dr. King who stood up for peace and marched on the streets - something to be commended. He was a Godly man. He followed the Holy Spirit wherever it took him, and may we be the same. May we be fearless. May we be as trusting in Our Father as a child.
My way of celebrating is to bring you news that can save someone’s ear(s), so they can continue to hear more good news.
If you or your parent(s) have hearing loss and are thinking of getting a COVID vaccine or booster, especially if you are over age 70, pause and consider a hearing test first, to evaluate nerve (i.e., neural) vs. conduction deficit. At least then, if hearing is SUDDENLY lost, you will know more about what to do.
For any medical procedure or intervention, physicians weigh the risk:benefit ratio and your physician is required to discuss “Informed Consent” with you. This is a specific discussion that relays the general risks and benefits to the public, plus the specific risks and benefits to you and your medical co-morbidities. Most doctors agree that if the risk outweighs the benefits, the procedure or intervention is not for you - because the Hippocratic Oath is to DO NO HARM. Doctors are not risk-takers.
Listen: Post-Vaccine Sudden Hearing Loss
The Invisible Disabilities™ Association has as this year’s emphasis, “Care in Motion”, so I’d like to exemplify that as applied to hearing loss.
Believe. Yesterday, it was pointed out to me that a friend suffered from the invisible disability named tinnitus, or ringing in the ear. Upon hearing this news, I did more than just read between the lines. I felt his pain. I knew from my previous traumatic brain injury the inflicted suffering of a tinnitus sufferer, because I had severe, bilateral (i.e., in both ears, versus unilateral, on one side) tinnitus for fifteen years. I believed him. He didn’t even have to explain his pain - I already knew.
I tried everything to get out of the grip that tinnitus had on my head.
After searching southern California for an answer, I ended up gradually de-conditioning from it, to the point where it decreased and mostly went away. Over time, I played background “white” noise, distracting away from it. If it recurs, it doesn’t bother me any more - it no longer persists louder than a bowling alley at the height of a Girl Scout competition (and the accompanying screams).

Support. I still remember the enormous frustration, perpetual isolation, persistent fatigue, and aggravated cognitive dysfunction, as well as the accompanying sleeplessness, anxiety, and depression of severe tinnitus. Because of that, and also wanting to be helpful, I spent a good part of the day writing a general review article on tinnitus, which frequently accompanies hearing loss. Both can occur after a vaccine. This is my way of supporting not only the complaint of tinnitus, but of sudden deafness, which can be cured.
Background
I covered the anatomy, symptoms, diagnostic exam and testing of tinnitus, as well as treatment options (SPOILER: there is no magic cure, but natural remedies may hold the best key, and there are many ways to “trick the brain” into diminishing the effect it has on the psyche):
This morning, I ran across this December 18, 2022 article by Dr. Peter McCullough, specifically on post-vaccine, SUDDEN hearing loss and deafness injury (not tinnitus, but still helpful). I copy it here for you and then further analyze SUDDEN post-vaccine hearing loss injury, which is often accompanied by tinnitus (my emphasis is in bold):
COVID-19 Vaccine Side Effects: "I Can't Hear You"
By Peter A. McCullough, MD, MPH
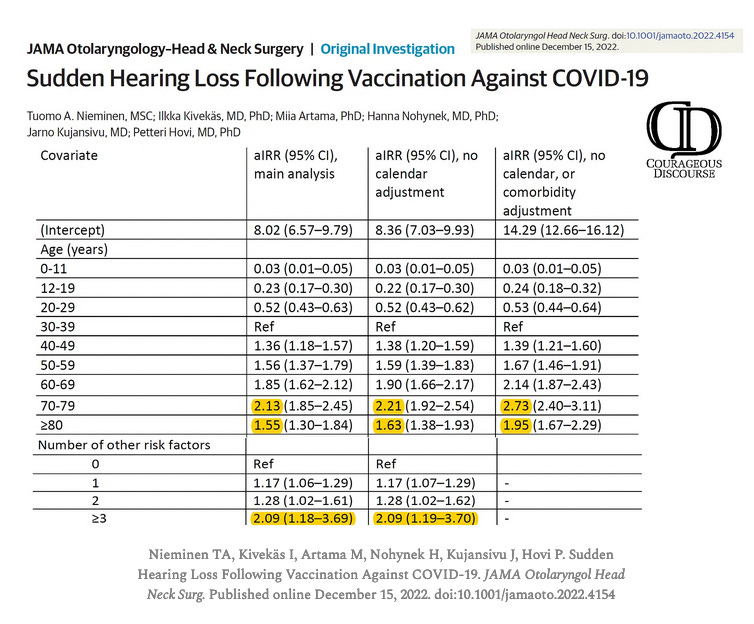
Risk of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss Doubled in the Elderly after Vaccination
Loss of hearing in the elderly is common affecting both the patient and the people around them trying to communicate. I have noticed many of my vaccinated elderly patients developing progressive hearing loss. Nieminen et al have conducted an extensive hearing assessment of patients in Finland after COVID-19 vaccination and compared them to the unvaccinated. The data suggested each successive shot increased risk for hearing loss. However, the most important results are in the supplemental tables which demonstrate the elderly and those with risk factors for hearing loss are pushed over the edge by COVID-19 vaccination.
Their risk for sudden and substantial loss of hearing is more than double those who wisely deferred on the vaccines. The Spike protein produced by the vaccines is a neurotoxin damaging nerves throughout the body and likely having more of an impact in nervous tissue which is already degenerated such as the auditory nerve. It is also possible the Spike protein incites inflammation leading to fibrosis in the tissue holding the stapes or stirrup which is a bone bone in the middle ear, the annular ligament, or the oval window all involved in the conduction of sound vibrations to the inner ear. If you have an elderly person in your circle who has been vaccinated, check on their hearing and do not fall behind on progressive hearing loss which if unchecked, can lead to social withdrawal and insidious depression.
If you find “Courageous Discourse” enjoyable and useful to your endeavors, please subscribe as a paying or founder member to support our efforts in helping you engage in these discussions with family, friends, and your extended circles.
Post-Vaccine Hearing Loss Injury
If your loved one complains of sudden hearing loss, be aware that this is a medical emergency with a 2-4 week window for steroids to reverse it. Afterward, deafness can be permanent.
Nerve Damage. The analysis of the above paper is this: if you get a vaccine when you already have nerve damage to the ear(s), the Spike protein is likely to be neurotoxic to it, targeting and making it worse.
If you can’t hear as well as you could before, consider the timing: did that happen after a shot? It could be a vaccine injury, but it doesn’t matter - get it treated ASAP so it can have the best chance of being reversed.
Fibrosis. Additionally, Spike protein may also inflame and/or cause fibrosis or scarring in the tiny ear bones, preventing them from vibrating and conducting sound vibrations that contribute to hearing.
This combination of aggravated nerve damage and bone tissue scarring is extremely detrimental to hearing, especially in the elderly.
Especially in those over age 70 with pre-existing hearing loss, a COVID vaccine may lead to sudden deafness. This is a Medical Emergency that if treated in the first 2-4 weeks, it may be reversible.
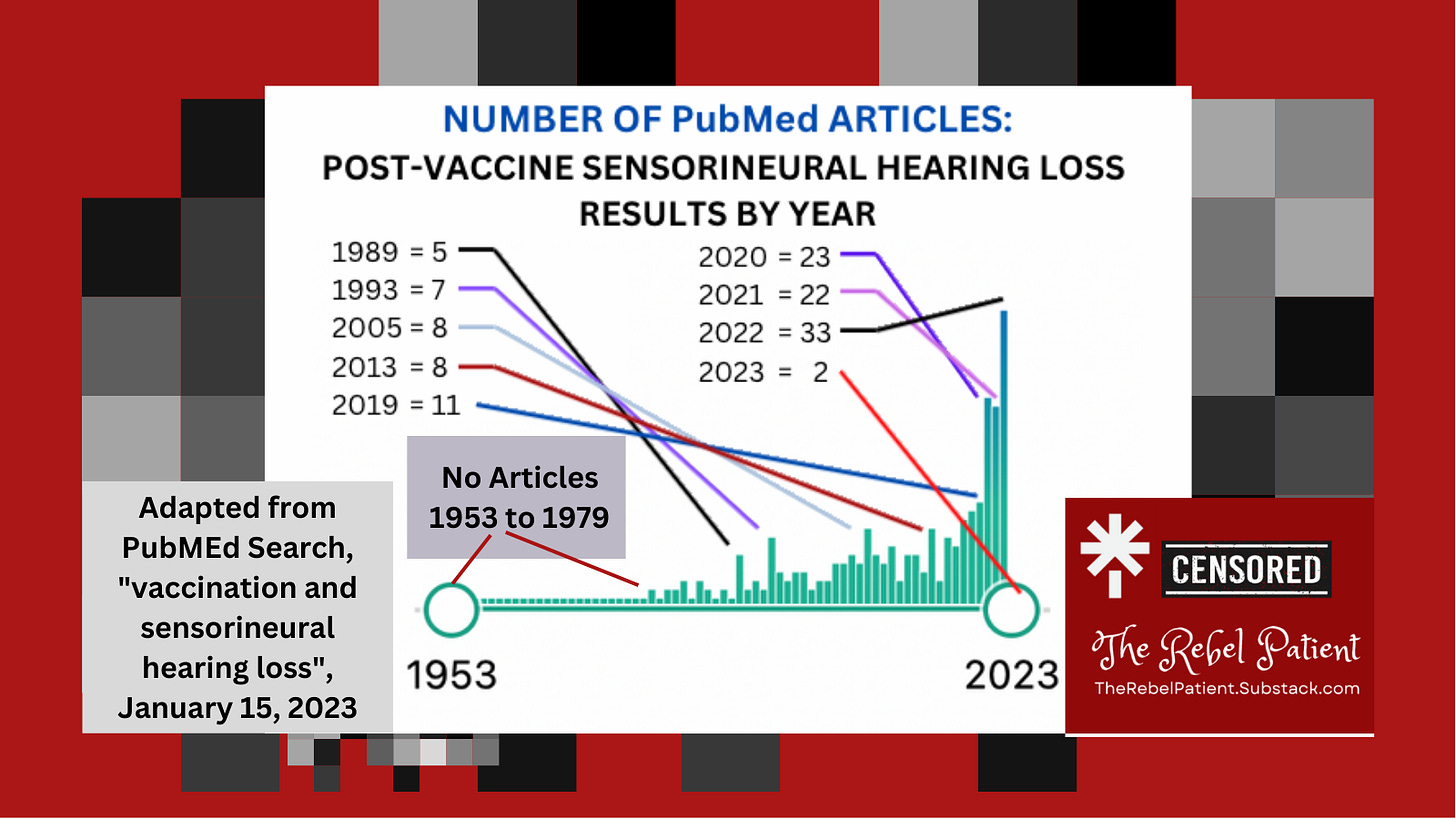
The Number of PubMed Articles Written on “Vaccine and Sensorineural Hearing Loss”
Running this search on PubMed shows 209 articles, with a significantly increased rate since the first article was written in 1978.
From 1953 to 1977, no articles were written. From 1978 to 1988, if an article was written, there were fewer than 3 per year, usually zero to one. From 1989 to 2018, under 10 articles were written per year.
The Number of PubMed Articles on hearing loss and COVID vaccines. In 2019, eleven articles were written. Then a spike occurred for 2020, 2021, and again for 2022. We should be on the lookout for sudden hearing loss and its emergency treatment, that can reverse deafness.
In 2020, 2021, and 2022, there were 23, 22, and 33 articles written, respectively, on vaccination and sensorineural hearing loss. As of January 15, only 2 articles have been written in 2023, a pace of perhaps 4/month for a projection of 48 by the end of the year, which would be another spike.
But it isn’t just the number of articles that is important - it is the gravity of the diagnosis.
Just what is sensorineural hearing loss, how bad can it be, and is it reversible?
Sudden Deafness = Sudden Sensorineuroal Hearing Loss (SSNHL)
A Medical Emergency
Sudden deafness, also known as sudden sensorineural hearing loss, is a medical emergency affecting several thousand people annually, most common between the ages of 40 to 60. It can be insidious, with no obvious cause, occur suddenly in one ear, or progressively worsen over three days.

Exam and Studies
Herrera et al provide a succinct analysis of the workup of sudden deafness":
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30093087/
Regarding diagnosis, if SSNHL is clinically suspected, the following diagnostic tests are mandatory: otoscopy, acumetry, tonal audiometry, speech audiometry, and tympanometry, to discount conductive causes. After clinical diagnosis has been established, and before treatment is started, a full analysis should be performed. An MRI should then be requested, ideally performed during the first 15 days after diagnosis, to discount specific causes and to help to understand the physiopathological mechanisms in each case. Although treatment is very controversial, due to its effect on quality of life after ISSNHL and the few rare adverse effects associated with short-term steroid treatment, this consensus recommends that all patients should be treated with steroids, orally and/or intratympanically, depending on each patient. In the event of failure of systemic steroids, intratympanic rescue is also recommended. Follow-up should be at day 7, and after 12 months.
Emergency Treatment
In a clinical trial involving more than 250 patients, Dr. Steven Rauch of Harvard Medical School and the Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary investigated patients from 16 USA medical centers. The trial was funded by NIH’s National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD). Results are in the May 25, 2011, issue of the Journal of the American Medical Association. Dr. Rauch stated,
“The comfort, cost and convenience of oral steroid treatment are preferable to intratympanic treatment, but injected steroids are an equally effective alternative for people who, for medical reasons, can’t take the oral steroids.
People with sudden deafness should discuss the risks and benefits of both treatments with their doctor.”
To restore hearing, prescribed steroid tablets like prednisone can be as effective as injected steroid into the inner ear. The oral steroid is often given in higher, then lower, tapered doses that are finished in about two weeks. The injection of steroid goes through and past the eardrum or tympanic membrane, into the middle ear.
If the patient is not treated within a 2- to 4-week time window, the hearing loss may become permanent.
Risks and Benefits of Steroid Treatment for Sudden Deafness
Oral Steroids.
Treats the whole body, not a single part. Side effects include elevated blood sugar, upset stomach, diarrhea, high blood pressure, jitteriness, anxiety, insomnia, increased appetite and mood changes. Not everyone wants to go on oral steroids, but it is a noninvasive method of treatment.
Injectable Steroid, Past the Eardrum.
This causes pain and possibly dizziness or vertigo, but delivers the steroid right where it needs to go. This may perforate the eardrum and cause severe ear pain, or may lead to an ear infection. There are no “whole body” side effects as listed above.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT)
A January, 2022 article showed that HBOT may augment medical therapy. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34709348/
WHAT I REALLY THINK
This news should be plastered everywhere. People with sudden hearing loss
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to The Rebel Patient™ to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.